In today’s dynamic digital marketing and online business landscape, comprehending your audience and their interactions with your website or app (GA4 Event Tracking and Audience Analysis) is pivotal for success. Enter Google Analytics 4 (GA4), your trusty ally on this journey. It equips you with potent tools to track user events and dissect your audience. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into two essential aspects of GA4, combining two Parts, to help you unlock valuable user insights.
PART 1: Deciphering GA4 Event Tracking
In this section, we’ll explore the world of event tracking in GA4. Events are user interactions with your website or app, and tracking them can provide you with invaluable information about how users engage with your content.
Understanding Events
Events in GA4 can be categorized into four main types, each serving a unique purpose:
- Automatically Collected Events: These are the basic interactions that GA4 tracks automatically, including pageviews, scroll tracking, and outbound clicks. They provide essential data about user engagement.
- Recommended Events: GA4 offers a list of suggested events that cover common user interactions such as pageviews, clicks, and engagement with videos and outbound links. Implementing these events can quickly enhance your understanding of user behavior.
- Enhanced Measurement Events: These events can be enabled to track interactions like site search, file downloads, and video engagement. Enabling enhanced measurement ensures you capture a broader range of user actions.
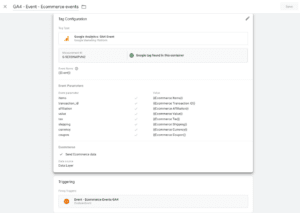
- Custom Events: The true power of GA4 lies in its ability to allow you to define custom events based on your unique business goals. Whether it’s tracking form submissions, button clicks, or specific user interactions, custom events are incredibly versatile.
Setting Up Event Tracking in GA4
1. Identify the Events to Track:
- Begin by identifying the user interactions you want to track. These can be anything from button clicks, downloads, video plays, form submissions, or any other action that’s important to your website or app’s goals.
2. Configure Event Parameters:
- Events can have associated parameters that provide more details about the event. Parameters help you segment and analyze event data effectively. For example, if you’re tracking button clicks, parameters could include the button’s name, location, or the page where the click occurred.
3. Implement Event Tracking:
- To implement event tracking, you have a few options:
a) Utilizing GA4 Code: You can add the GA4 tracking code with event data directly to your website or app’s code. Here’s an example of how you might send an event to GA4 using JavaScript for a button click:
gtag(‘event’, ‘button_click’, {
‘event_category’: ‘User Interaction’,
‘event_label’: ‘Homepage Button’,
});
In this example, when a user clicks a button on the homepage, the event ‘button_click’ is sent to GA4 with event category and event label parameters.
b) Leveraging Google Tag Manager (GTM): If you prefer a user-friendly interface without needing to modify your site’s code, you can set up event tracking in Google Tag Manager (GTM). GTM allows you to create tags that send event data to GA4 without direct coding. Here’s how you might set up a tag in GTM to track a button click:
- Create a new tag and choose GA4 Configuration as your tag type.
- Select your GA4 configuration and specify the event name (e.g., ‘button_click’) along with any parameters (e.g., event category and event label).
- Define a trigger for when the tag should fire (e.g., when the button is clicked).
Examples of Event Tracking
Let’s look at some examples of event tracking in GA4:
1. Tracking File Downloads:
- Suppose you want to track when users download PDF files on your website. You can use event tracking to achieve this. In your code or GTM, you would send an event with the name ‘file_download’ when a user clicks a download link, along with parameters specifying the file name, file type, and the page it was downloaded from. Example (using JavaScript):
gtag(‘event’, ‘file_download’, {
‘event_category’: ‘Downloads’,
‘event_label’: ‘ebook.pdf’,
‘file_type’: ‘PDF’,
‘page_location’: ‘/resources’
});
2. Video Play Tracking:
- If you have embedded videos on your website and want to know how many users are watching them, you can track video plays. Send an event with the name ‘video_play’ when a video starts playing, including parameters like video title, category, and duration.
Example (using GTM):
- Create a GTM tag that sends the ‘video_play’ event when the video player is clicked, and include parameters like ‘video_title’ and ‘video_duration.’
3. Form Submission Tracking:
- You can track form submissions to understand which forms are most popular or effective. Send an event with the name ‘form_submission’ when a user submits a form, and include parameters like ‘form_name’ and ‘form_category.’
Example (using GTM):
- Create a GTM trigger to detect when a form submission occurs and send the ‘form_submission’ event with relevant parameters.
By setting up event tracking in GA4, you can gain deeper insights into how users interact with your website or app. It enables you to measure the effectiveness of specific features and campaigns and make data-driven decisions to enhance user experiences and achieve your business goals.
Event Reports and Analysis
Once you’ve set up event tracking, GA4 provides a range of reports to help you analyze user interactions and their impact on your goals. These reports include:
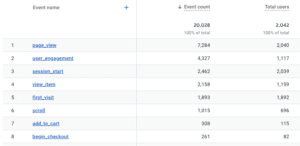
- Event Count Report: This report shows the total counts of each event, helping you understand which actions are most popular among your users.
- Event Parameter Reports: These reports allow you to explore event data further by diving into event parameters. You can see which variations of a specific event are the most popular, helping you tailor your content and marketing efforts accordingly.
- Top Events Report: This report provides an overview of the most frequently occurring events on your website or app. It’s useful for identifying which user interactions are the most significant in your audience’s journey.
PART 2: Audience and User Properties
In this section, we’ll delve into audience analysis and the use of user properties in GA4. Understanding your audience is essential for tailoring your content and marketing efforts effectively.
Audience Building
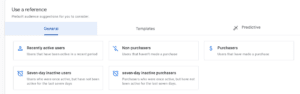
1. Default Audiences:
GA4 offers several default audiences that can serve as a foundation for understanding your audience. These default audiences include:
- New Users: Users who have visited your site or app for the first time.
- Returning Users: Users who have visited your site or app more than once.
- Engaged Users: Users who have spent significant time on your site or app and interacted with your content.
2. Custom Audiences:
Create custom audiences by defining specific criteria based on user behavior, demographics, technology usage, and more. Custom audiences help you segment your user base for more targeted marketing and analysis.
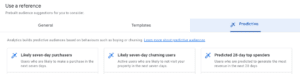
3. Predictive Audiences:
GA4 incorporates machine learning to create predictive audiences. These audiences can help you identify potential high-value users based on their past interactions and behavior patterns.
User Properties
User properties allow you to collect additional information about your users, providing a deeper understanding of your audience. Some common user properties include:
- Demographics: Information such as age, gender, and location.
- Interests: Insights into user interests, such as technology, travel, or fitness.
- User IDs: Unique identifiers for users, which are valuable for cross-device tracking and personalized experiences.
By segmenting your audience based on these properties, you can gain deeper insights into user behavior. This, in turn, enables you to deliver more personalized content and targeted marketing campaigns.
Conclusion: Unleashing GA4’s Full Potential
In this comprehensive guide, we’ve only scratched the surface of what Google Analytics 4 (GA4) has to offer. Our journey into the world of GA4 is far from over. This introductory guide has laid the foundation, and there’s so much more to explore and discover in the realm of user insights and data-driven decision-making.
In the end, GA4 is more than just an analytics platform; it’s your trusted partner on the path to data-driven success. As we embark on this exciting journey, remember that the power of GA4 lies not just in the data it collects, but in how you use that data to make informed decisions. We’re here to help you every step of the way.